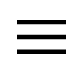Overview
Busan is the 2nd largest city and the number one trading hub in Korea, with a population of 3.3 million and a total area of 770.2 square kilometers as of 2024. Since it opened the first Korean international port in 1876, the city has become the hub of trade, commerce and industry.
Global events including the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Conference, the Busan International Film Festival, the Busan International Fireworks Festival, and various other sea festivals are held each year, and it is a tourist destination with Asia’s largest department store, Haeundae beach, and a yachting center.
Located on the southern tip of Korea, it is a historic city that served as a temporary capital during the Korean War, where refugees who fled from the north built villages.
Population
From its opening in 1876, the port city of Busan quickly developed into a hub of trade, commerce and industry. This development resulted in a rapid increase in its population, which had already reached 200,000 by 1936. A major leap in Busan's population came with the breakout of the Korean War, which resulted in an endless stream of people into the city. As a result, the population of Busan exceeded 1 million by the end of 1955. Another factor that spurred the population increase was the government policy for economic growth. People from urban areas kept streaming into the city for jobs. By the end of 1994, there were approximately 4 million people who called Busan their home. Since 1995, the population has slowly begun to decrease. As of December 2021, Busan was home to 3,396,109 people, a decrease of 42,601 compared to 2020. The male population was at 49 percent, while the female population was at 51 percent. The population of foreign residents living in Busan stood at 45,729, an increase of 1,035 compared to 2020.
Climate
Busan is located at the southeastern most tip of the Korean peninsula and in the mid-latitude temperate zone, which has seasonal winds. It has four seasons: spring, summer, fall and winter. The annual average temperature is 14.9°C. The annual average precipitation is 1,441.9mm. Busan has strong winds compared to other areas in Korea. Spring begins in March and ends in late June. Cherry blossom trees bloom in late March and the temperature is very comfortable from April to June. The rainy season at the end of June and July signals the beginning of the coming summer heat. The highest mean temperatures of around 32°C are at the end of July through mid-August. Fall is from early September through late-November. The weather is nice and cool at this time because of the continental high atmospheric pressure. Winter starts by the end of November and continues until February, but Busan rarely receives any snowfall. The average winter temperature is 3.8°C. Tourists can enjoy Busan throughout all seasons because of the nice weather and beautiful scenery. In summer, the city, particularly Haeundae and Gwangalli beaches are crowded with visitors who come to enjoy the beautiful and laidback lifestyle Busan residents have come to love.
City Environment
Busan, a city of beautiful mountains, rivers and the sea, is also an important cultural city. With the Nakdonggang River bordering the city and picturesque scenery, like that found in Haeundae gaining nationwide attention, the city serves as a major nexus of cultural activities around the region. Busan also is the first international port city in Korea. Its location enables the city to serve as a main gateway for the Korean Peninsula and the entire Northeast Asian region.
Business-Friendly City
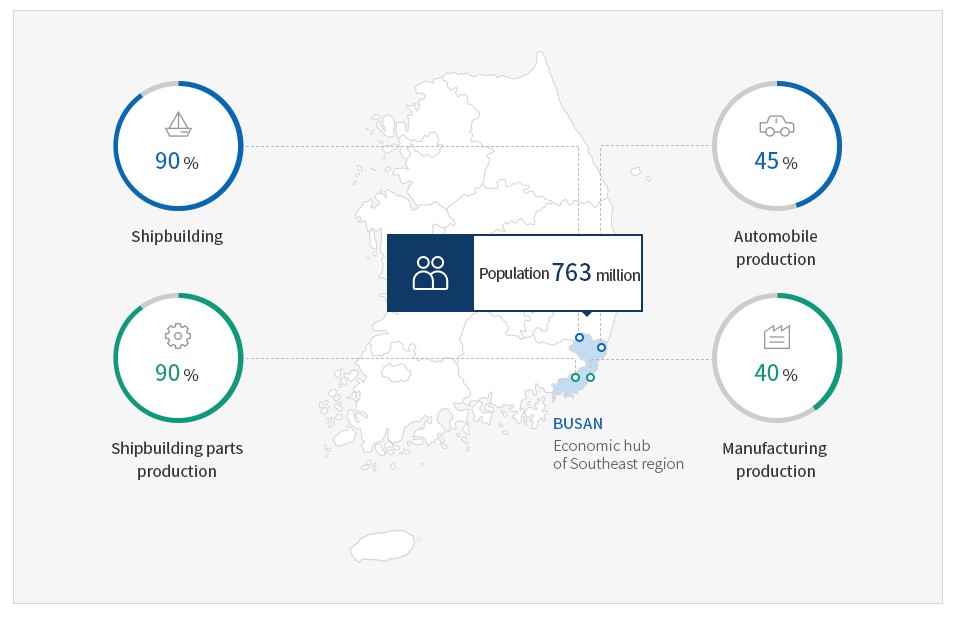
Busan is the logistics and economic hub of the southeast region in Korea. As an industrial hub of Korea with a population of 7.63 million, it handles 90% of shipbuilding and shipbuilding parts production, 45% of automobile production and 40% of manufacturing.
Location
Geographically, Busan has the Straits of Korea to its south; Ulsan to the north; and Gimhae to the West. Cities that share almost the same latitude with Busan include Jinhae and Gwangju in Korea, as well as Tokyo, Algiers and Oklahoma City internationally. Busan is eight hours ahead of GMT. As for its geopolitical location, the city is located at the Southern tip of a strip that connects Asia, Siberia and Europe. It also serves as a main gateway to the Pacific Ocean. This strategic location places the city at the center of international sea transportation.
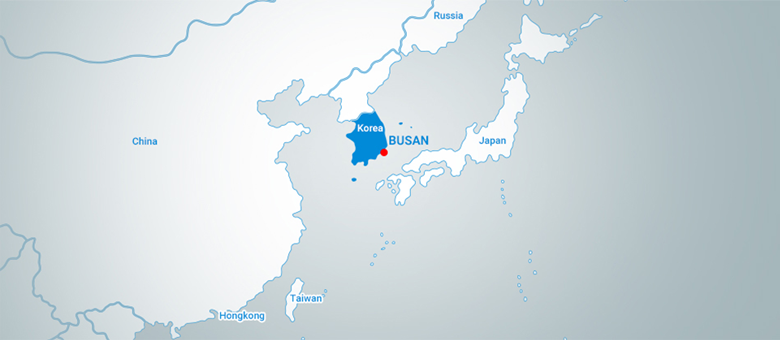
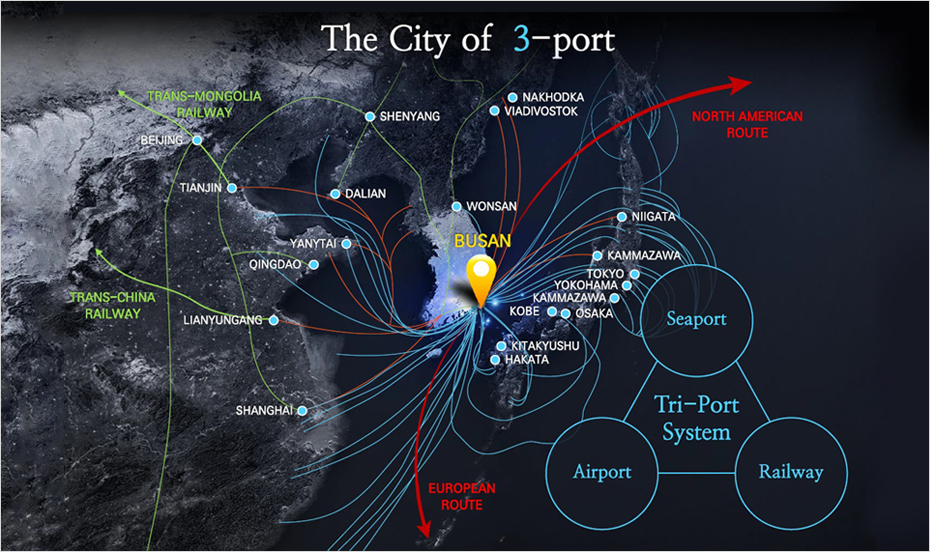
Strategic Place for Global Logistics
When the North Pole Route—a shortcut that connects Europe with Asia—is developed in 2030, the distance from Busan to Europe and from Busan to North America will be reduced by 40% and 30%, respectively. In addition, Busan is the key starting point of the future Silk Road Express (SRX), a railway that will connect Busan with Europe through China and Russia. As such, this will enable Busan to grow from a logistics city in Northeastern Asia to the mecca of world logistics.